觀察者模式與發布/訂閱模式區別
編輯:JavaScript基礎知識
在翻閱資料的時候,有人把觀察者(Observer)模式等同於發布(Publish)/訂閱(Subscribe)模式,也有人認為這兩種模式還是存在差異,而我認為確實是存在差異的,本質上的區別是調度的地方不同。
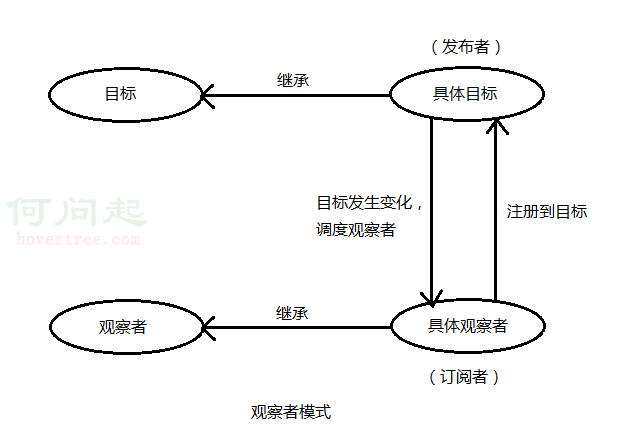
觀察者模式
比較概念的解釋是,目標和觀察者是基類,目標提供維護觀察者的一系列方法,觀察者提供更新接口。具體觀察者和具體目標繼承各自的基類,然後具體觀察者把自己注冊到具體目標裡,在具體目標發生變化時候,調度觀察者的更新方法。
比如有個“天氣中心”的具體目標A,專門監聽天氣變化,而有個顯示天氣的界面的觀察者B,B就把自己注冊到A裡,當A觸發天氣變化,就調度B的更新方法,並帶上自己的上下文。

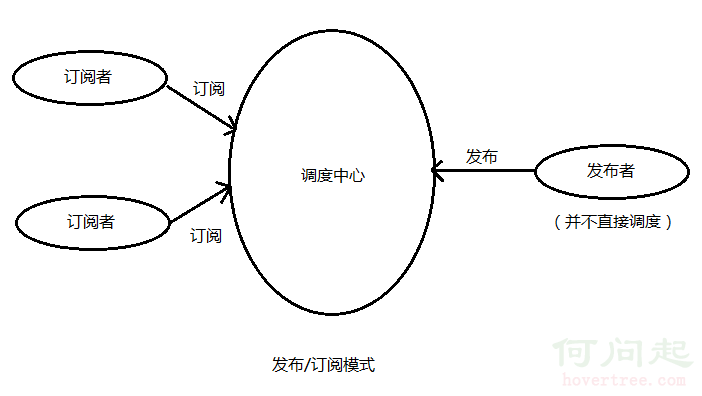
發布/訂閱模式
比較概念的解釋是,訂閱者把自己想訂閱的事件注冊到調度中心,當該事件觸發時候,發布者發布該事件到調度中心(順帶上下文),由調度中心統一調度訂閱者注冊到調度中心的處理代碼。
比如有個界面是實時顯示天氣,它就訂閱天氣事件(注冊到調度中心,包括處理程序),當天氣變化時(定時獲取數據),就作為發布者發布天氣信息到調度中心,調度中心就調度訂閱者的天氣處理程序。

總結
1. 從兩張圖片可以看到,最大的區別是調度的地方。
雖然兩種模式都存在訂閱者和發布者(具體觀察者可認為是訂閱者、具體目標可認為是發布者),但是觀察者模式是由具體目標調度的,而發布/訂閱模式是統一由調度中心調的,所以觀察者模式的訂閱者與發布者之間是存在依賴的,而發布/訂閱模式則不會。
2. 兩種模式都可以用於松散耦合,改進代碼管理和潛在的復用。
附錄
觀察者模式實現代碼(JavaScript版):
//觀察者列表
function ObserverList(){
this.observerList = [];
}
ObserverList.prototype.add = function( obj ){
return this.observerList.push( obj );
};
ObserverList.prototype.count = function(){
return this.observerList.length;
};
ObserverList.prototype.get = function( index ){
if( index > -1 && index < this.observerList.length ){
return this.observerList[ index ];
}
};
ObserverList.prototype.indexOf = function( obj, startIndex ){
var i = startIndex;
while( i < this.observerList.length ){
if( this.observerList[i] === obj ){
return i;
}
i++;
}
return -1;
};
ObserverList.prototype.removeAt = function( index ){
this.observerList.splice( index, 1 );
};
//目標
function Subject(){
this.observers = new ObserverList();
}
Subject.prototype.addObserver = function( observer ){
this.observers.add( observer );
};
Subject.prototype.removeObserver = function( observer ){
this.observers.removeAt( this.observers.indexOf( observer, 0 ) );
};
Subject.prototype.notify = function( context ){
var observerCount = this.observers.count();
for(var i=0; i < observerCount; i++){
this.observers.get(i).update( context );
}
};
//觀察者
function Observer(){
this.update = function(){
// ...
};
}
發布/訂閱模式實現代碼(JavaScript經典版):
var pubsub = {};
(function(myObject) {
// Storage for topics that can be broadcast
// or listened to
var topics = {};
// An topic identifier
var subUid = -1;
// Publish or broadcast events of interest
// with a specific topic name and arguments
// such as the data to pass along
myObject.publish = function( topic, args ) {
if ( !topics[topic] ) {
return false;
}
var subscribers = topics[topic],
len = subscribers ? subscribers.length : 0;
while (len--) {
subscribers[len].func( topic, args );
}
return this;
};
// Subscribe to events of interest
// with a specific topic name and a
// callback function, to be executed
// when the topic/event is observed
myObject.subscribe = function( topic, func ) {
if (!topics[topic]) {
topics[topic] = [];
}
var token = ( ++subUid ).toString();
topics[topic].push({
token: token,
func: func
});
return token;
};
// Unsubscribe from a specific
// topic, based on a tokenized reference
// to the subscription
myObject.unsubscribe = function( token ) {
for ( var m in topics ) {
if ( topics[m] ) {
for ( var i = 0, j = topics[m].length; i < j; i++ ) {
if ( topics[m][i].token === token ) {
topics[m].splice( i, 1 );
return token;
}
}
}
}
return this;
};
}( pubsub ));
本文為原創文章,轉載請保留原出處,方便溯源,如有錯誤地方,謝謝指正。
- 上一頁:快樂的JS正則表達式(一)
- 下一頁:淺談JavaScript閉包
小編推薦
熱門推薦