物體運動原理:通過改變物體的位置,而發生移動變化。
方法:
1.運動的物體使用絕對定位
2.通過改變定位物體的屬性(left、right、top、bottom)值來使物體移動。例如向右或左移動可以使用offsetLeft(offsetRight)來控制左右移動。
步驟:
1、開始運動前,先清除已有定時器 (因為:是連續點擊按鈕,物體會運動越來越快,造成運動混亂)
2、開啟定時器,計算速度
3、把運動和停止隔開(if/else),判斷停止條件,執行運動
一.定時器
在javascritp中,有兩個關於定時器的專用函數,它們是:
1.倒計定時器:timename=setTimeout("function();",delaytime);
2.循環定時器:timename=setInterval("function();",delaytime);
function()是定時器觸發時要執行的是事件的函數,可以是一個函數,也可以是幾個函數,或者javascript的語句也可以,單要用;隔開;delaytime則是間隔的時間,以毫秒為單位。
倒計時定時器就是在指定時間後觸發事件,而循環定時器就是在間隔時間到來時反復觸發事件,其區別在於:前者只是作用一次,而後者則不停地作用。
倒計時定時器一般用於頁面上只需要觸發一次的的情況,比如點擊某按鈕後頁面在一定時間後跳轉到相應的站點,也可以用於判斷一個浏覽者是不是你的站點上的“老客”,如果不是,你就可以在5秒或者10秒後跳轉到相應的站點,然後告訴他以後再來可以在某個地方按某一個按鈕就可以快速進入。
循環定時器一般用於站點上需要從復執行的效果,比如一個javascript的滾動條或者狀態欄,也可以用於將頁面的背景用飛雪的圖片來表示。這些事件需要隔一段時間運行一次。
有時候我們也想去掉一些加上的定時器,此時可以用clearTimeout(timename) 來關閉倒計時定時器,而用clearInterval(timename)來關閉循環定時器。
二.運動研究
1.運動:勻速運動(讓物體動起來)
對定時器的使用
給DIV加絕對定位
offsetLeft
問題:到達某個特定位罝停符
解決:做判斷,符合條件時關掉定時器(存定時器timer)
速度變慢(一般不動時間,而是改數字-速度)
用變量存速度
問題:取7時,offsetLeft沒有等於300的時候,div停不下來
解決:>=300 //停在 301
問題:到300後點擊按鈕還繼續走
原因:點擊按鈕,執行函數,開定時器(執行當前函數一至少執行一次)
解決:加else (沒有到達目標之前才執行)
問題:連續點擊,速度變快
原因:每點擊一次就開一個定時器,點擊幾次就有幾個定時器同時工作
解決:保證每次只有一個定時器工作,先cearlnterval ()
示例1,
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>分享到</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:150px; height:200px; background:green; position:absolute; left:-150px;}
#div1 span {position:absolute; width:20px; height:60px; line-height:20px; background:blue; right:-20px; top:70px;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
oDiv.onmouseover=function ()
{
startMove(0);
};
oDiv.onmouseout=function ()
{
startMove(-150);
};
};
var timer=null;
function startMove(iTarget)
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
clearInterval(timer);
timer=setInterval(function (){
var speed=0;
if(oDiv.offsetLeft>iTarget)
{
speed=-10;
}
else
{
speed=10;
}
if(oDiv.offsetLeft==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(timer);
}
else
{
oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<span>分享到</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:

示例2,淡入淡出:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>淡入淡出</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:200px; height:200px; background:red; filter:alpha(opacity:30); opacity:0.3;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
oDiv.onmouseover=function ()
{
startMove(100);
};
oDiv.onmouseout=function ()
{
startMove(30);
};
};
var alpha=30;
var timer=null;
function startMove(iTarget)
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
clearInterval(timer);
timer=setInterval(function (){
var speed=0;
if(alpha<iTarget)
{
speed=10;
}
else
{
speed=-10;
}
if(alpha==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(timer);
}
else
{
alpha+=speed;
oDiv.style.filter='alpha(opacity:'+alpha+')';
oDiv.style.opacity=alpha/100;
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1"></div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:
勻速運動的停止條件
距離足夠近
示例3,勻速運動的停止條件:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>勻速運動的停止條件</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:100px; height:100px; background:red; position:absolute; left:600px; top:50px;}
#div2 {width:1px; height:300px; position:absolute; left:300px; top:0; background:black;}
#div3 {width:1px; height:300px; position:absolute; left:100px; top:0; background:black;}
</style>
<script>
var timer=null;
function startMove(iTarget)
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
clearInterval(timer);
timer=setInterval(function (){
var speed=0;
if(oDiv.offsetLeft<iTarget)
{
speed=7;
}
else
{
speed=-7;
}
if(Math.abs(iTarget-oDiv.offsetLeft)<=7)
{
clearInterval(timer);
oDiv.style.left=iTarget+'px';
}
else
{
oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="到100" onclick="startMove(100)" />
<input type="button" value="到300" onclick="startMove(300)" />
<div id="div1"></div>
<div id="div2"></div>
<div id="div3"></div>
</body>
</html>
2.變速運動(緩沖運動)
逐漸變慢,最後停止
距離越遠速度越大
速度有距離決定
速度=(目標值-當前值)/縮放系數
如果沒有縮放系數t速度太大,瞬間到達終點.沒有過程
問題:並沒有真正到達300
原因:速度只剩0.9 //像素是屏幕能夠顯示的最/J庫位,並不會四捨五入掉
Math.ceil ()向上取整
Math.floor ()向下取整
問題:向左走,又差一塊--Math.floor ()
判斷:三目 speed=speed>0 ? Math.ceil ( speed ): Math.floor ( speed )
示例,緩沖運動:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>緩沖運動</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:100px; height:100px; background:red; position:absolute; left:600px; top:50px;}
#div2 {width:1px; height:300px; position:absolute; left:300px; top:0; background:black;}
</style>
<script>
function startMove()
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
setInterval(function (){
var speed=(300-oDiv.offsetLeft)/10;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px';
document.title=oDiv.offsetLeft+','+speed;
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="開始運動" onclick="startMove()" />
<div id="div1"></div>
<div id="div2"></div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:

3.多物體運動
多個div ,鼠標移入變寬
運動框架傳參obj,知道讓哪個物體動起來
用到緩沖一定要取整
問題:div沒運動回去 //清除前一個定時器
原因:只有一個定時器
解決:加物體上的定時器,使每個物體都有一個定時器。定時器作為物體屬性
多個div淡入淡出
首先關閉物體上的定時器
經驗:多物體運動框架所有東西都不能共用
問題:不是因為定時器,而是因為alpha
解決:作為屬性附加到物體上 /不以變量形式存在
offset 的 bug
加border變寬
offsetWith並不是真正的width ,它獲取的是盒模型尺寸
解決:躲著 寬度扔到行間,parselnt ( oDiv.style.width )
進一步解決: getStyle ( obj, name ) currentStyle , getComputedStyle
加border ,只要offset就有問題 去掉offset
示例,多物體運動:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>無標題文檔</title>
<style>
div {width:100px; height:50px; background:red; margin:10px; border:10px solid black;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var aDiv=document.getElementsByTagName('div');
for(var i=0;i<aDiv.length;i++)
{
aDiv[i].timer=null;
aDiv[i].onmouseover=function ()
{
startMove(this, 400);
};
aDiv[i].onmouseout=function ()
{
startMove(this, 100);
};
}
};
function startMove(obj, iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer=setInterval(function (){
var speed=(iTarget-obj.offsetWidth)/6;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
if(obj.offsetWidth==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
}
else
{
obj.style.width=obj.offsetWidth+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:
4.任意值運動
任意值運動的單位分為透明度和px。
px單位的任意值
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>無標題文檔</title>
<style>
div {width:200px; height:200px; margin:20px; float:left; background:yellow; border:10px solid black; font-size:14px;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var oDiv1=document.getElementById('div1');
oDiv1.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'height', 400);};
oDiv1.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'height', 200);};
var oDiv2=document.getElementById('div2');
oDiv2.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'width', 400);};
oDiv2.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'width', 200);};
var oDiv3=document.getElementById('div3');
oDiv3.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'fontSize', 50);};
oDiv3.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'fontSize', 14);};
var oDiv4=document.getElementById('div4');
oDiv4.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'borderWidth', 100);};
oDiv4.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'borderWidth', 10);};
};
function getStyle(obj, name)
{
if(obj.currentStyle){return obj.currentStyle[name];}
else{return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[name];}
}
function startMove(obj, attr, iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer=setInterval(function (){
var cur=parseInt(getStyle(obj, attr));
var speed=(iTarget-cur)/6;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
if(cur==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
}
else
{
obj.style[attr]=cur+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">變高</div>
<div id="div2">變寬</div>
<div id="div3">safasfasd</div>
<div id="div4"></div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:
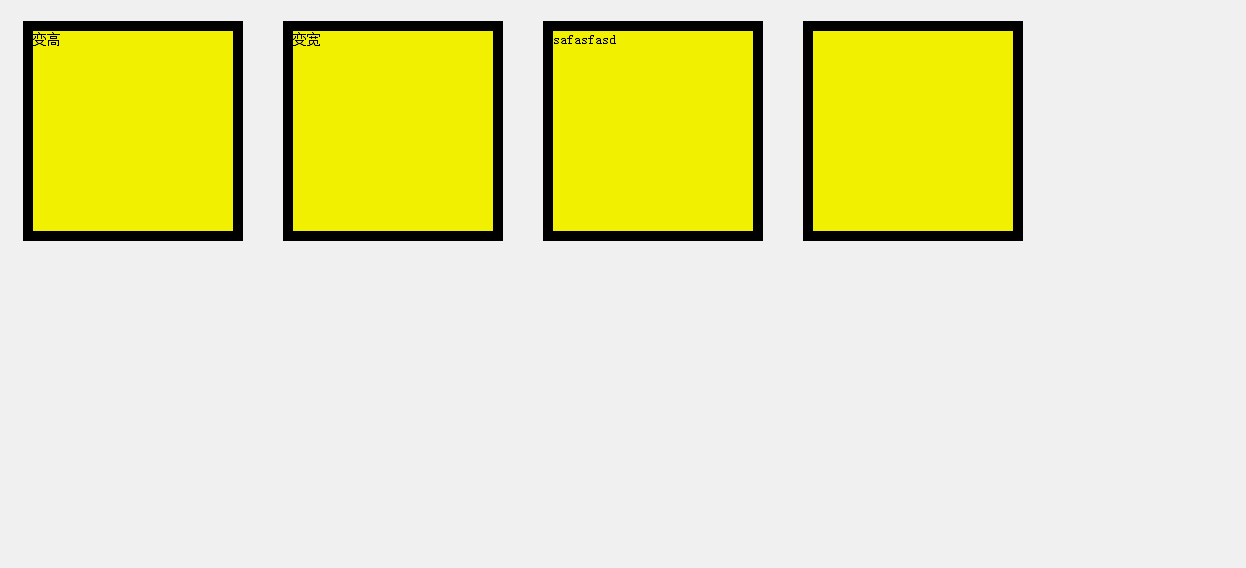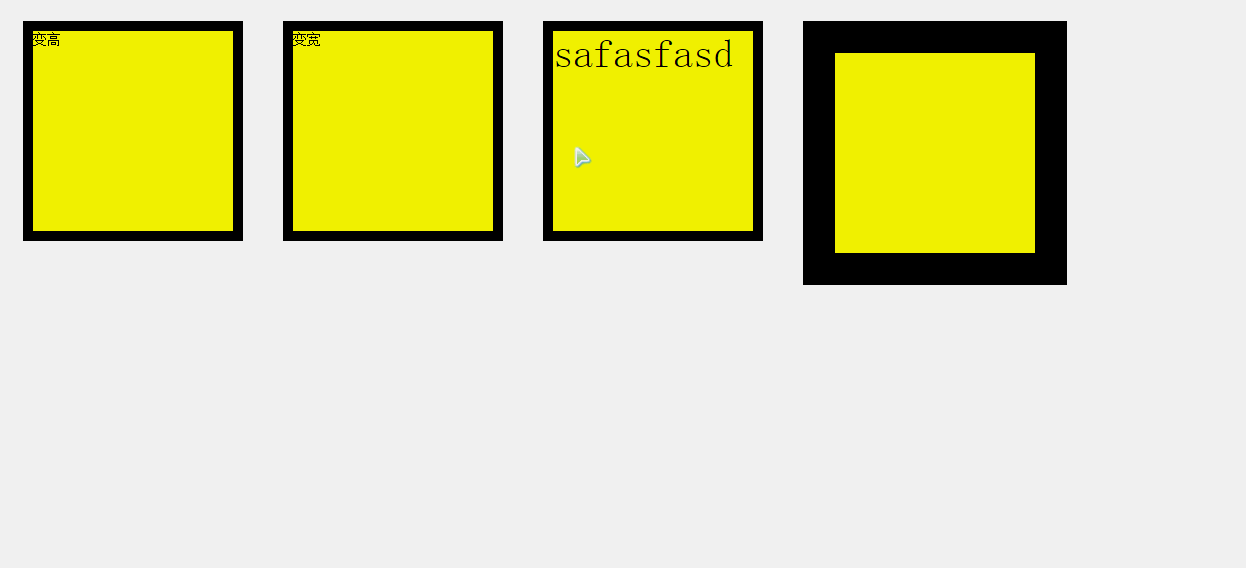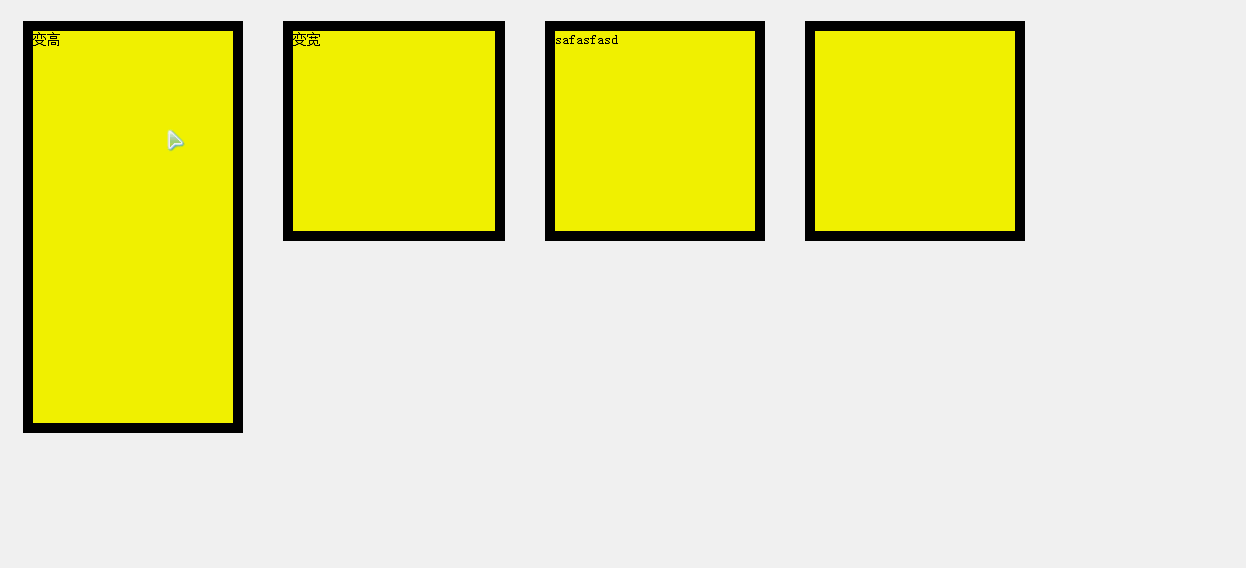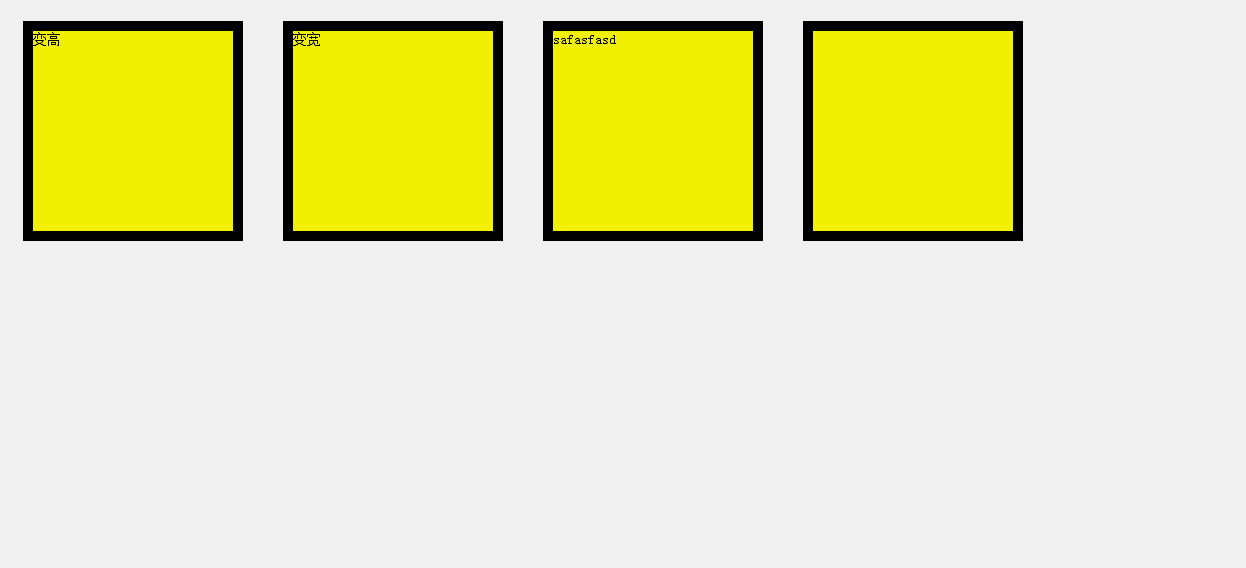
透明度的任意值,需要做判斷:
判斷
var cur=0
if ( attr== 'opacity '){
cur=parseFloat ( getStyle ( obj, attr)) *100
}else{
}
設置樣式判斷
if ( attr== 'opacity '){
obj.style.fiIter = 'alpha ( opacity: '( cur+speed ) + ')'
obj.style.opacity= ( cur+speed ) /100
}else{
}
5.鏈式運動
多出來的一個參數,只有傳進去的時候才調用
鼠標移入變寬,結束之後彈出abc
先橫向展開.再以向展開
鼠標移出,先變回不透明,變矮,變窄
三.封裝運動框架(源碼下載:https://github.com/jingwhale/jsmove/blob/master/move.js)
基於以上的分析與總結,封裝運動框架move.js如下:
function getStyle(obj, name)
{
if(obj.currentStyle)
{
return obj.currentStyle[name];
}
else
{
return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[name];
}
}
function startMove(obj, json, fnEnd)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer=setInterval(function (){
var bStop=true; //假設:所有值都已經到了
for(var attr in json)
{
var cur=0;
if(attr=='opacity')
{
cur=Math.round(parseFloat(getStyle(obj, attr))*100);
}
else
{
cur=parseInt(getStyle(obj, attr));
}
var speed=(json[attr]-cur)/6;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
if(cur!=json[attr])
bStop=false;
if(attr=='opacity')
{
obj.style.filter='alpha(opacity:'+(cur+speed)+')';
obj.style.opacity=(cur+speed)/100;
}
else
{
obj.style[attr]=cur+speed+'px';
}
}
if(bStop)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
if(fnEnd)fnEnd();
}
}, 30);
}
move.js運動框架基本滿足現在網頁上所有動畫的需求(不包括css3)。
四.應用應用
1,完成如下效果:

js代碼如下:
<script src="move.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('play');
var aBtn=oDiv.getElementsByTagName('ol')[0].getElementsByTagName('li');
var oUl=oDiv.getElementsByTagName('ul')[0];
var now=0;
for(var i=0;i<aBtn.length;i++)
{
aBtn[i].index=i;
aBtn[i].onclick=function ()
{
now=this.index;
tab();
};
}
function tab()
{
for(var i=0;i<aBtn.length;i++)
{
aBtn[i].className='';
}
aBtn[now].className='active';
startMove(oUl, {top: -150*now});
}
function next()
{
now++;
if(now==aBtn.length){now=0;}
tab();
}
var timer=setInterval(next, 2000);
oDiv.onmouseover=function (){clearInterval(timer);};
oDiv.onmouseout=function (){timer=setInterval(next, 2000);};
};
</script>
應用2,完成如下效果:

代碼如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>無標題文檔</title>
<style type="text/css">
.....
</style>
<script type="text/javascript" src="move.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function ()
{
var oBtn=document.getElementById('but');
var oBottom=document.getElementById('zns_bottom');
var oBox=document.getElementById('zns_box');
var oBtnClose=document.getElementById('btn_close');
oBox.style.display='block';
var initBottomRight=parseInt(getStyle(oBottom, 'right'));
var initBoxBottom=parseInt(getStyle(oBox, 'bottom'));
oBox.style.display='none';
oBtn.onclick=openHandler;
oBtnClose.onclick=closeHandler;
function openHandler()
{
startMove(oBottom, {right: 0}, function (){
oBox.style.display='block';
startMove(oBox, {bottom: 0});
});
oBtn.className='but_hide';
oBtn.onclick=closeHandler;
}
function closeHandler()
{
startMove(oBox, {bottom: initBoxBottom}, function (){
oBox.style.display='none';
startMove(oBottom, {right: initBottomRight}, function (){
oBtn.className='but_show';
});
});
oBtn.onclick=openHandler;
}
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
......
</body>
</html>
源碼下載:https://github.com/jingwhale/jsmove
以上所述就是本文的全部內容了,希望大家能夠喜歡。